Power reliability has become a serious concern for homeowners across the United States. Extreme weather events, aging infrastructure, and grid strain increase the likelihood of outages that last hours or even days.
A properly designed home backup system protects comfort, safety, and daily routines during those disruptions.
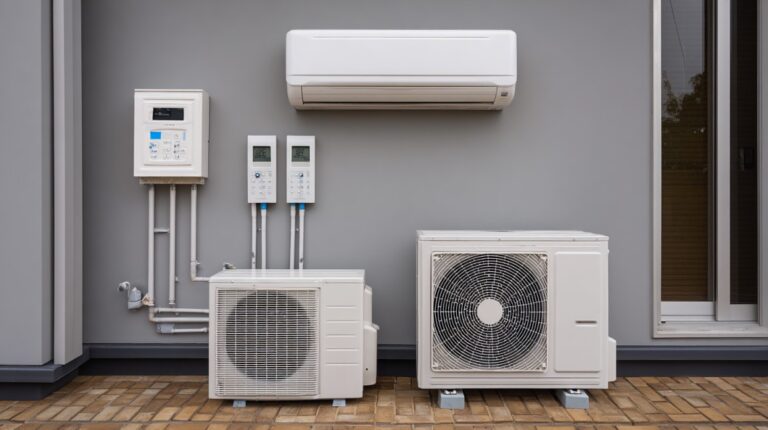
Loss of power quickly affects indoor temperature control, food storage, and essential electronics. High summer temperatures turn outages into health risks, especially when cooling systems stop working.
That is why we would like to talk about how to build a home backup system that can actually help you run your A/C.
System Components
Reliable performance during a power outage depends on how well individual parts work together. Each component in a home backup system serves a specific purpose that directly affects safety, runtime, and the ability to operate high-demand appliances like air conditioning.
Careful selection at this stage prevents system limitations later.
Batteries
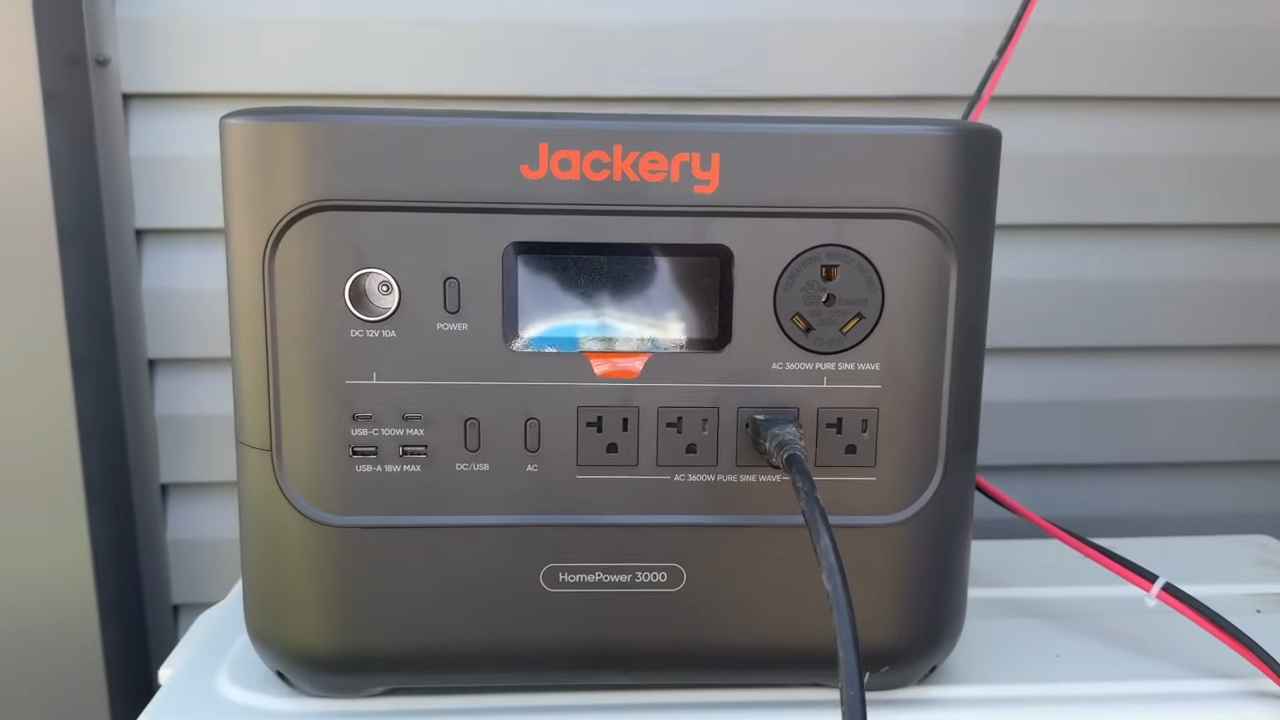

Energy storage forms the foundation of any modern backup solution. Lithium battery technology plays a central role in modern backup power design because it supports repeated use without rapid capacity loss.
Lithium iron phosphate battery packs deliver long cycle life, strong safety performance, and modular expansion options that suit residential needs.
- High cycle counts that support daily charging and discharging
- Improved thermal stability compared to older lithium chemistries
- Modular configurations that allow capacity growth over time
Energy storage allows a home backup system to capture electricity ahead of an outage or store power produced by solar panels. Stored energy then supplies appliances when grid power disappears, keeping essential loads operational without interruption.
Battery capacity directly influences how long cooling systems and other appliances continue operating. Larger battery banks extend runtime, especially when paired with efficient load management.
Inverters
View this post on Instagram
Power stored in batteries remains unusable for household appliances until converted. Inverters convert stored DC energy into standard AC power used by household appliances. Proper inverter selection matters greatly when air conditioning sits on the load list.
Cooling systems place heavy demands on electrical systems due to both continuous power draw and short-term startup surges.
- Continuous wattage required during steady A/C operation
- Surge capacity needed during compressor startup
- Total combined load when multiple appliances run simultaneously
Sizing an inverter incorrectly leads to tripped systems, shutdowns, or the inability to start the A/C compressor. Reliable home backup system performance depends on matching inverter capacity to real-world load demands rather than estimated averages.
Charge Controllers and Chargers
Charging hardware manages how energy enters battery packs and protects internal components. Charge controllers regulate solar input, while chargers handle grid-based charging when utility power remains available.
- Prevents overcharging that degrades battery cells
- Balances voltage across battery modules
- Limits heat buildup during high-input charging periods
Correct charging management extends battery lifespan and improves safety. Stable charging behavior supports consistent performance during extended outages, especially when batteries cycle frequently during hot weather events.

Transfer Switch and Interconnection Hardware
Electrical interconnection equipment allows safe integration between backup power and a home’s electrical panel. Transfer switches isolate backup circuits and ensure electricity flows only where intended.
- Preventing backfeed into utility lines
- Separating essential loads from non-critical circuits
- Maintaining compliance with electrical safety standards
Professional-grade hardware ensures compliance with electrical codes and protects technicians and homeowners. A home backup system relies on this layer for safe operation during outages and normal grid conditions.
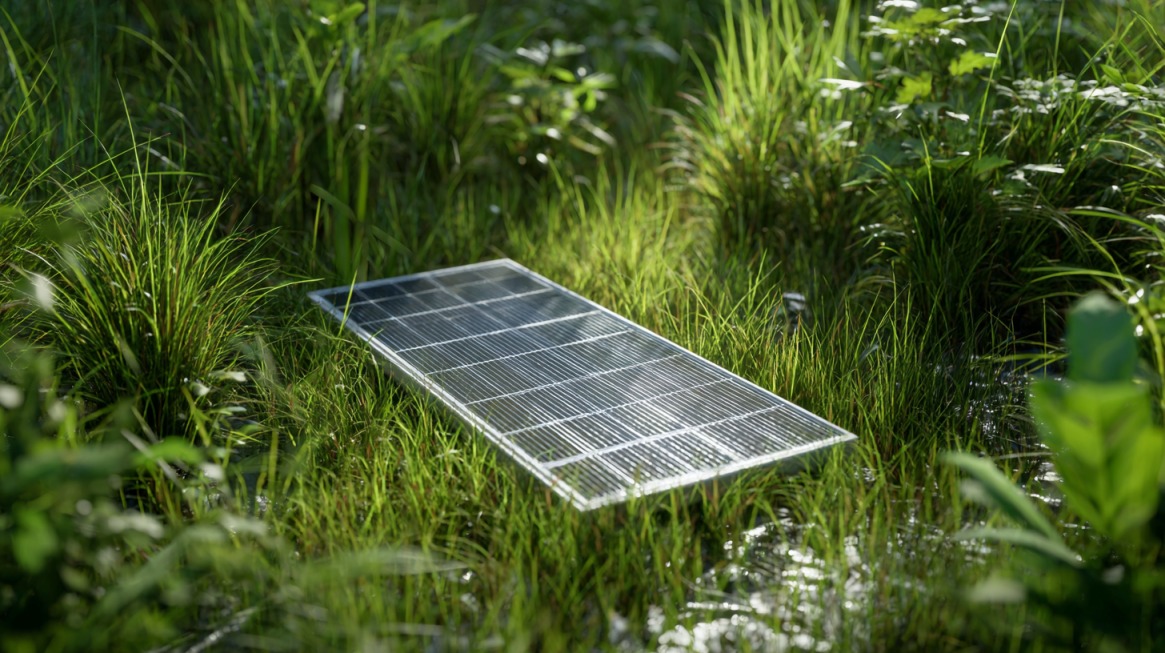
Optional Solar Panels
Renewable generation adds another layer of reliability. Solar panels provide a renewable charging source for battery systems and reduce reliance on stored energy alone.
- Recharges batteries during daylight hours
- Extends runtime during prolonged outages
- Reduces overall grid electricity usage
Solar integration adds a higher level of independence. Battery systems continue charging during outages, extending runtime and reducing stress on stored capacity. Pairing solar panels with a home backup system supports both emergency use and long-term energy savings.

Step-by-Step Build Process
System assembly follows a logical sequence that ensures proper sizing, safety, and long-term usability. Skipping steps or rushing decisions often results in performance limitations later.
Assess Backup Goals
Planning begins with identifying critical appliances. Air conditioning often tops the list, followed by refrigerators, lighting, medical equipment, and communication devices.
Accurate calculations prevent system overload. Power requirements must be calculated accurately, accounting for both steady operation and startup demand.
- Running wattage of each appliance
- Startup surge for motors and compressors
- Duration each load must operate during an outage
Honest load assessment prevents disappointment during an outage and ensures a home backup system meets real needs rather than assumptions.
Choose System Capacity
View this post on Instagram
Battery sizing determines runtime length. Products such as EcoFlow DELTA Pro allow expansion through additional battery modules, supporting multi-day outages when properly configured.
Inverter sizing must handle peak demand without strain. Air conditioning startup draws require careful attention, especially when combined with other loads. Adequate inverter headroom ensures stable operation under heavy loads and avoids shutdowns during critical moments.
Select and Source Components
Component selection defines reliability and scalability. System design can follow a custom-built approach or a plug-and-play solution, depending on technical comfort level and installation goals.
- Battery bank sized for desired runtime
- Inverter capable of supporting peak loads
- Transfer switch for safe panel connection
- Charger and wiring matched to system ratings
Turnkey solutions simplify installation and reduce compatibility concerns. Modular designs allow future expansion as energy needs grow.
Wiring and Installation
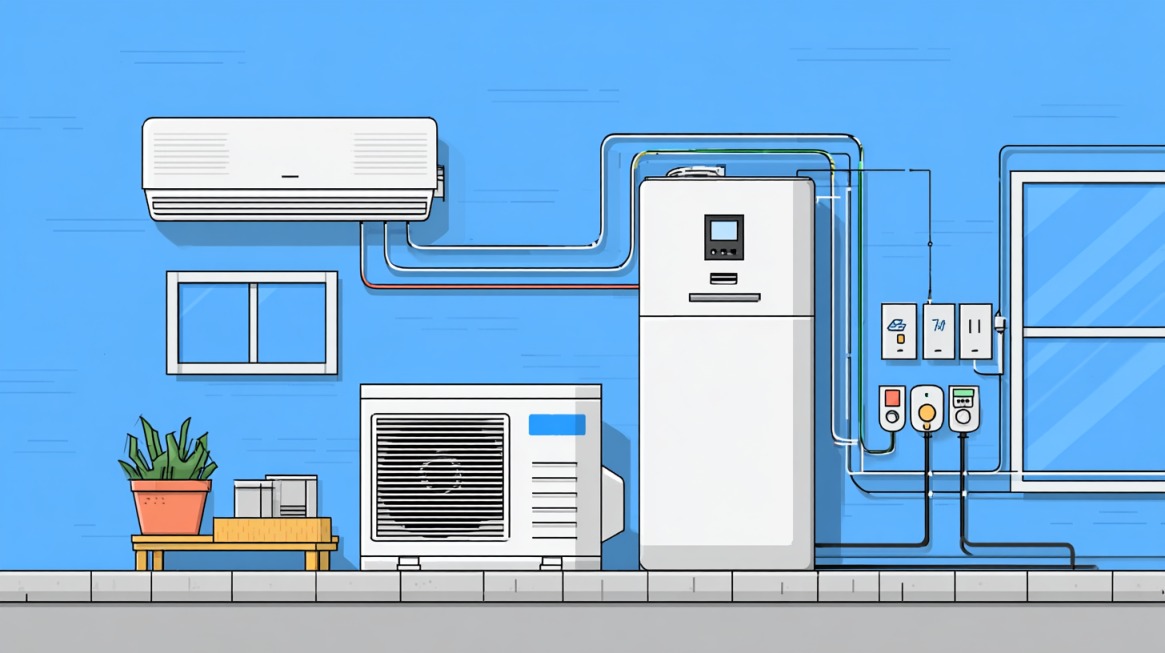
Electrical installation connects all components into a functional system. Panel-level electrical work involves serious safety risks and requires proper training.
- Correct grounding and bonding
- Proper load separation
- Compliance with local electrical codes
Professional installation protects equipment and occupants while preserving warranty coverage on many system components.
Testing and Commissioning
System readiness depends on thorough testing. Performance testing verifies that all components work together as intended.
Simulated outages confirm air conditioning startup behavior and steady operation under load. Testing also identifies wiring issues or capacity shortfalls early, allowing corrections before a real emergency occurs.
Solar Integration
Solar power increases the value of a home backup system by extending runtime during outages. Daytime generation reduces battery drain and allows continuous operation of essential loads even during extended grid failures.
Solar panels paired with battery storage provide practical independence during prolonged outages. Charging continues as long as sunlight remains available, offering reliable cooling support during heat waves when outages are most disruptive.
Cost, Sizing, and Runtime Estimation
Investment level depends on performance goals. System cost varies based on battery capacity, inverter quality, solar panel size, and installation labor.
- Longer runtime for air conditioning
- Support for additional household loads
- Reduced reliance on grid restoration timelines
Sizing guidance depends on expected load and outage duration. Expandable battery systems reaching dozens of kilowatt-hours support extended cooling operation when paired with solar input.
Runtime depends on total load and energy storage size. Solar input significantly improves runtime, especially during daytime outages when cooling demand often peaks.
Battery Backup vs. Generators
Technology choice shapes outage experience. Battery-based solutions operate quietly and produce no exhaust fumes, making them suitable for residential neighborhoods. Maintenance needs remain minimal, and integration with solar power enables continuous recharging.
Generators provide proven power but rely on fuel availability and create noise and emissions. Fuel storage and refueling logistics add complexity during extended outages, especially during regional emergencies.
A modern home backup system offers a cleaner and more convenient option for homeowners prioritizing comfort and reliability without ongoing fuel management.

Summary
Running air conditioning during a power outage remains achievable with proper planning and equipment selection.
Batteries, inverters, and optional solar panels work together to deliver reliable performance.
Advances in lithium battery technology and solar integration improve reliability, safety, and convenience. A well-designed home backup system supports comfort and peace of mind during grid disruptions
Next steps involve evaluating loads, selecting components or a turnkey solution, and testing performance before an outage occurs.

